Indexing Pipeline
This section is an overview of how to take a collection to a state in which it can be queried. This process is intentionally broken down into several steps, with a bunch of independent tools performing different tasks. This is because we want the flexibility of experimenting with each individual step without recomputing the entire pipeline.
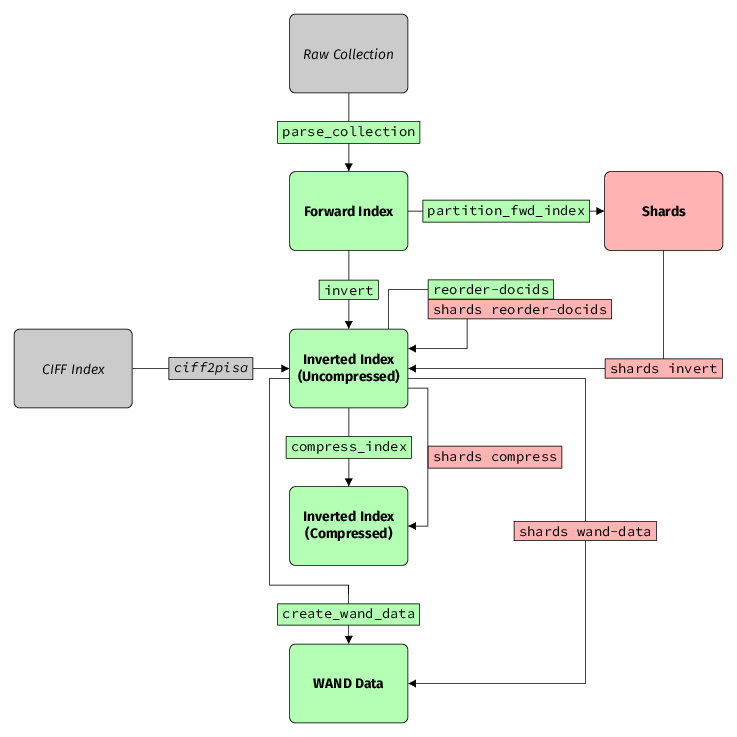
External Resources
Raw Collection
The raw collection is a dataset containing the documents to index. A
collection is encoded in one of the supported
formats that stores a list of document
contents along with some metadata, such as URL and title. The
parse_collection tool takes a collection as an input and parses it to
a forward index (see Forward Index). See
Parsing for more details.
CIFF Index
This is an inverted index in the Common Index File Format.
It can be converted to an uncompressed PISA index (more information below)
with the ciff2pisa tool.
Forward Index
A forward index is the output of the parse_collection tool.
It represents each document as a list of tokens (terms) in the order of their appearance.
To learn more about parsing and the forward index format, see Parsing.
Inverted Index
An inverted index is the most fundamental structure in PISA. For each term in the collection, it contains a list of documents the term appears in. PISA distinguishes two types of inverted index.
Uncompressed / Binary Collection
The uncompressed index stores document IDs and frequencies as 4-byte integers.
It is an intermediate format between forward index and compressed inverted index.
It is obtained by running invert on a forward index.
To learn more about inverting a forward index, see Inverting.
Optionally, documents can be reordered with reorder-docids to obtain another
instance of uncompressed inverted index with different assignment of IDs to documents.
More on reordering can be found in Document Reordering.
Compressed
An uncompressed index is large and therefore before running queries, it must be compressed with one of many available encoding methods. It is this compressed index format that is directly used when issuing queries. See Compress Index to learn more.
WAND Data
This is a special metadata file containing additional statistics used during query processing. See Build additional data.
Shards
PISA supports partitioning a forward index into subsets called shards.
Structures of all shards can be transformed in bulk using shards command line tool.
To learn more, read Sharding.